By 2025, managing storage has become crucial as game installations often exceed 100GB. While upgrading hardware provides a solution, compatibility challenges arise with internal drives requiring specific setup steps. External options simplify setup but still demand proper configuration for optimal performance.
Whether using internal or external SSDs on computers or consoles, proper initialization ensures seamless functionality. Follow these platform-specific guidelines for Windows, macOS, and gaming systems to maximize storage efficiency.
1. Format SSDs for Windows and Mac OS
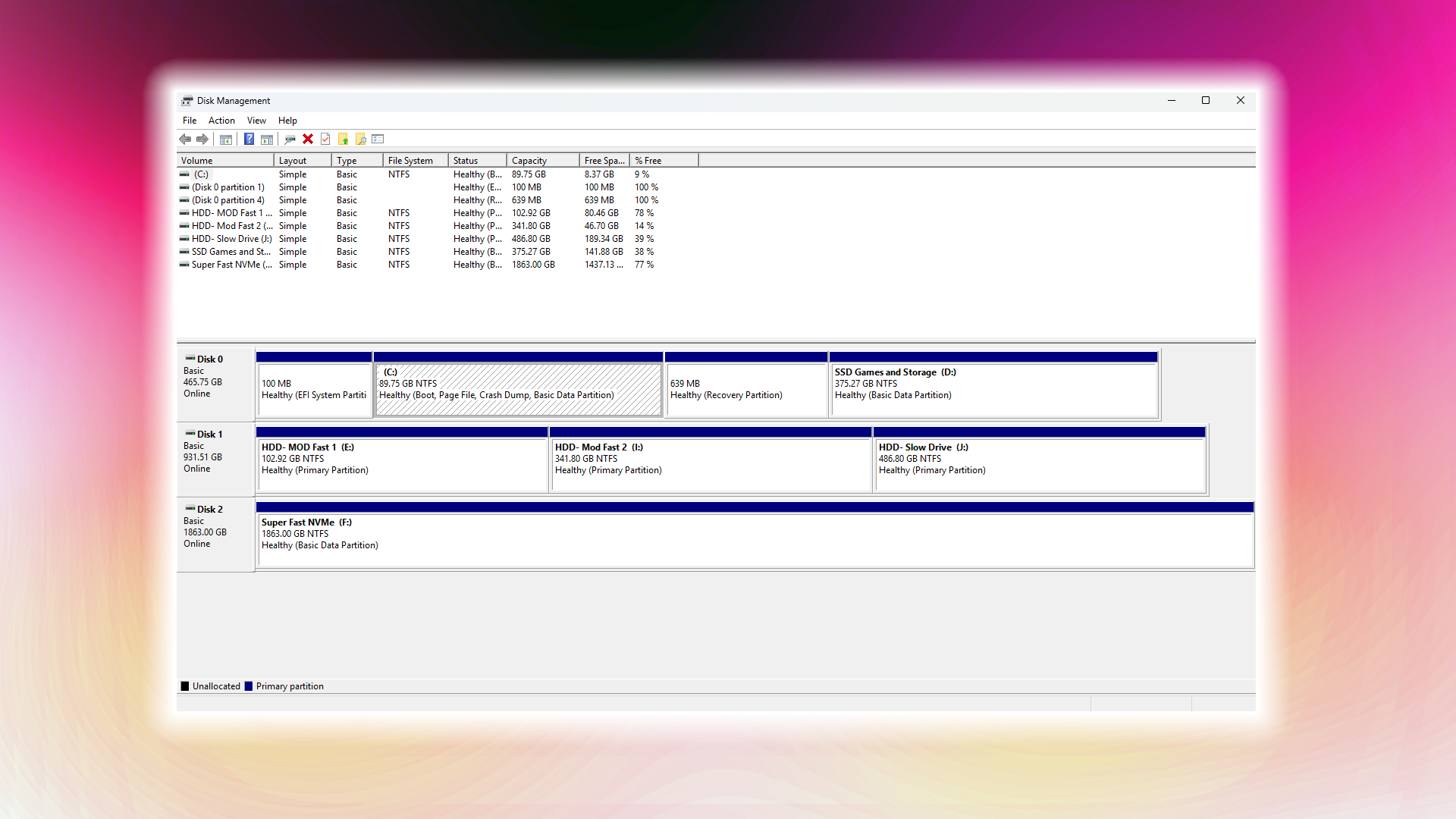
While some external drives function immediately, internal storage devices require manual preparation. Both operating systems employ similar principles with distinct workflows.
Windows Systems:
- Access disk tools via Windows+X shortcut and choose Disk Management
- Identify unallocated SSD space, right-click to initiate formatting
- Configure settings: NTFS format, 4096-byte allocation, enable Quick Format option
- External drives allow direct formatting through File Explorer shortcuts
macOS Configuration:
- Access Disk Utility through Applications > Utilities
- Enable Show All Devices in the View menu
- Select target drive and initiate erase function
- Choose GUID Partition Map with APFS format for modern compatibility
2. Formatting SSDs for Gaming Consoles
Modern gaming platforms enforce specific storage protocols. When default connections fail, manual intervention resolves detection issues.
PlayStation 5 Setup:
- Connect SSD to rear USB-C port for optimal bandwidth
- Navigate through Settings > Storage > USB Extended Storage
- Select format option to establish exFAT partition structure
Xbox Series X|S Preparation:
- Insert drive into USB 3.0 port meeting speed requirements
- Accept formatting prompt upon connection detection
- Customize drive label and finalize NTFS configuration
Verdict
Always safeguard existing data through backups before formatting procedures. Fresh internal drives necessitate preparation for system recognition, while cross-platform compatibility requires attention to file system specifications.

